Topaz Description.
Properties, Structure and Morphology.
The description of topaz is mainly based on information taken from the "Lehrbuch der Mineralogie" by Hans Jürgen Rösler
Chemical formula: Al2 (F,OH)2 [SiO4]
Name: most likely the name comes from "Topazios", an old Greek name for an island in the Red Sea
Crystal structure: orthorhombic, space group Pbnm, nesosilicate, aside SiO4-tetrahedra the structure contains zigzag-chains of edge-linked Al-octahedra
Crystal Structure of Topaz
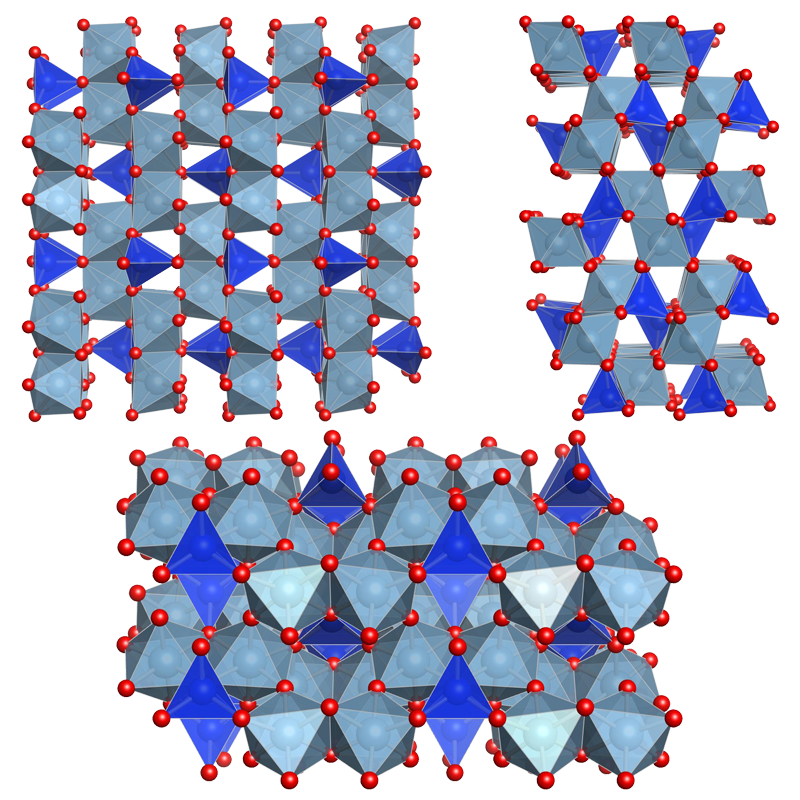
The representation of the crystal structure is provided for information purposes only and is based on the CIF-file, which contains all parameters as result of the structure analysis performed by Wunder et al.:
Wunder B, Rubie D C, Ross C R, Medenbach O, Seifert F, Schreyer W American Mineralogist 78 (1993) 285-297
Synthesis, stability, and properties of Al2SiO4(OH)2: A fully hydrated analogue of topaz
All single views were created by use of Vesta:
K. Momma and F. Izumi, "VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data," J. Appl. Crystallogr., 44, 1272-1276 (2011).
Physical Properties of Topaz:
Colors: Colorless, Yellow, Orange, Pink, Red, Violet, Blue, Green
Luster: Vitreous (Glassy)
Hardness: 8
Specifiv Gravity (g/cm³): 3.5 - 3.7
Cleavage: perfect parallel to the basal plane (001)
Optik: birefringent, Δ=0,010, biaxial positive
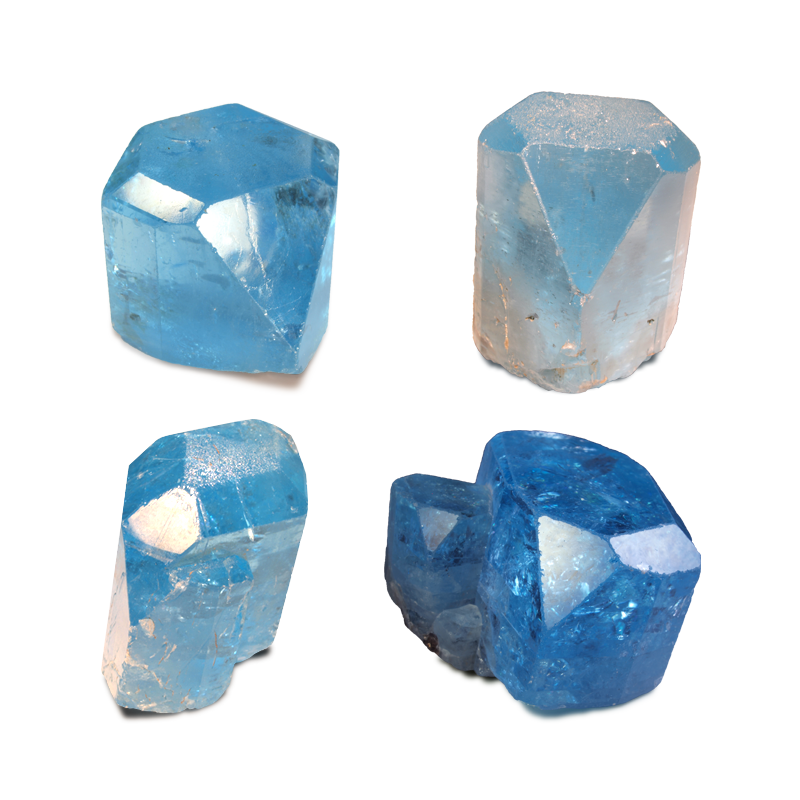
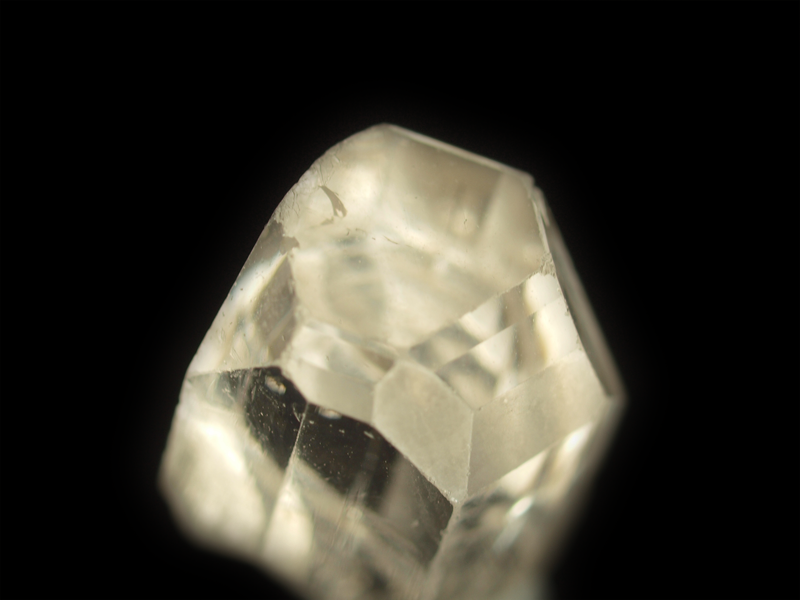
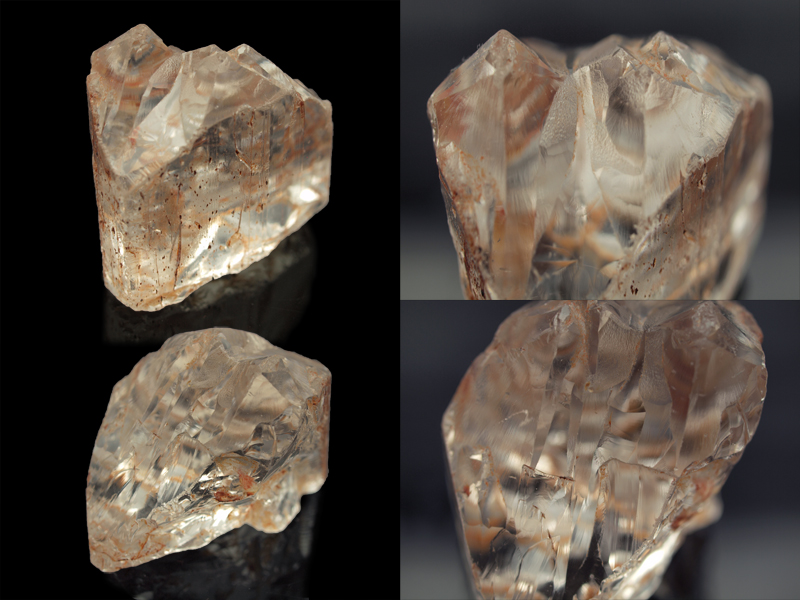
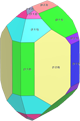
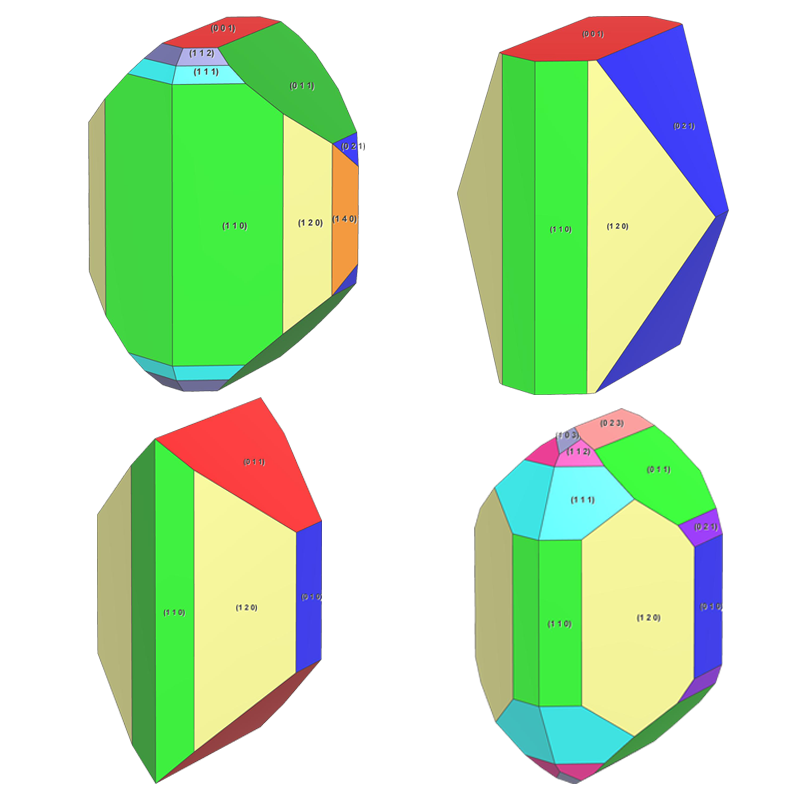
Topaz - Morphology
Topaz crystals are often idiomorphic and may contain numerous faces
Here some topaz crystals of different habit (created with Vesta) and some photographs of topaz crystals